Junkers Ju
87 Stuka
Dornier Do 215
Junkers Ju-188
Dornier Do
17
Dornier Do
335 Pfeil
Junkers Ju 88
Messerschmitt Bf
109
Messerschmitt Me110
Messerschmitt Me
262
Focke-Wulf Fw
200 Condor,
Heinkel He
111
Focke-Wulf Fw
190,
Junkers Ju
52
USAF Plane
List
USN
FIGHTERS
LIST OF
PLANES US AIR FORCE WW2
USN WW2
Torpedo Bomber -
Douglas
TBD-1 Devastator
USN WW2
Fighters:
P-38
LIGHTNING
F-82 TWIN
MUSTANG
REPUBLIC
P-47 THUNDERBOLT
NORTH
AMERICAN P-51 MUSTANG
Boeing B-17
Flying Fortress,
Boeing B-29
Superfortress
B-24 D
Liberator
B-25
Mitchell,
Martin B-26
Marauder
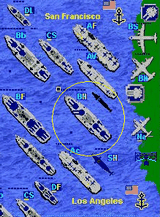
Battleship Game - WW2 Naval
Strategy: the best choice among aircraft carrier games
and submarine games and battleship games.
Missions and Scenarios:
Pearl Harbor Game
Atlantic Game 1943
Sink Cruisers Game
Midway Game
Iwo Jima Game
US Marines Game
Luftwaffe Game Pacific
Torpedo Game Boats
Bismarck Game Pacific
Destroy RAF Game
Okinawa
Us Navy Submarine Game
Fleet Submarines Game
Kamikaze Game
U Boat Game
Singapore Game
Swordfish Hunt
Patrol Boats
Air Supremacy
Alert
Battleships Game
Java
Defense
Fleet Cruisers Game
Atlantic Island
Coral Sea Game
Iron Sea
Mykonos
Imperial Ocean
Long Convoy
Skagerrak
Target Los Angeles
West Pacific Game
Pacific War Game
Leyte Transport
Emperor Hirohito
Normandy Game
South Pacific Game
Destroy USAF Game
Submarine Games
US Navy Game
Free Hunt Doenitz Game
Free Hunt Spruance Game
Free Hunt Halsey Game
Imperial Navy I
Royal Navy Game
Free Hunt Pearl Harbor Games
Midway II
Kriegsmarine I
Brisbane Convoy
Clear West Coast
Fall Of Australia
Battle For Leyte
Conquer Of Japan
HMAS Perth
Road To Okinawa
Orange Ports
Emperor Defense
Prince Of Wales
San Bernardino
Pacific Race
Heavy Duty
Tokio Express
Operation Sidney
Bomber Operation
Conquer Of Italy
Heavy Cruiser Game
Frigate Hunt
Santa Cruz
Lamansh Game
Azores Transport
Norway Convoy
Invasion
Grossadmiral
Norway Ports
Drang Nach Ost
Convoy Pk30
Ciano Defense
Sir John Tovey
Free Hunt Andrews
Germans On Pacific
Silent Hunt
Antigua
Return To Midway
Kriegsmarine Game II
Royal Air Force Game
F. Hunt Lancaster
Jamamoto Game
Free Hunt USN
Free Hunt Japan
Free Hunt RAAF
Free Hunt U Boat Game
Free Hunt Aircraft Carriers Game
Free Hunt Hawaii
Free Hunt Yamato Game
Free Hunt Iwo Jima Game
Free Hunt Pacific Game
Free Hunt Torpedos
Free Hunt Convoy
Free Hunt Germany
Free Hunt Germany II
Free Hunt Italy
Free Hunt Malaya
Free Hunt Subs Game
Free Hunt B-26 Game
Free Hunt USN 1944
Devil Island
Dragoon Carriers
|
Junkers Ju87
The Junkers Ju 87
or Stuka was the most famous Sturzkampfflugzeug
(German dive bomber) in World War II, instantly
recognisable by its inverted gull-wings and fixed
undercarriage.
The Stuka's design included some
innovative features, including an automatic pull-up
system to ensure that the plane recovered from its attack
dive even if the pilot blacked out from the high
acceleration, and wind-powered sirens on the wheel covers
that wailed during dives to scare its victims.
The Stuka was sturdy, accurate, and
very effective, but also slow, unmaneuverable,
underarmed, and vulnerable to enemy fighters. The Germans
learned in the Battle of Britain that air superiority
must be obtained before ground attack aircraft could be
effectively used. After the Battle of Britain, the Stuka
was little used in western Europe, but it remained
effective further south where Allied fighters were in
short supply (notably in the attacks on Crete and Malta,
and was used in vast numbers on the Eastern Front,
although the steady rise in Soviet airpower as the war
progressed meant that Stuka squadrons suffered very heavy
losses.
Over 5700 Ju87 Stukas were built.
Ju87 General
Characteristics
(Models
not listed include the Ju.87C, intended for use on the
aircraft carrier Graf
Zeppelin, the Ju.87R long-range version of the
Ju.87B, the Ju.87C naval derivative of the Ju.87B, the
Ju.87H disarmed versions of the equivalent D-models for
use as trainers, and the Ju.87K export models.)
| Type: |
Ju87A-1 |
Ju87 B-1 |
Ju87-D-1 |
Ju-87 G-1 |
| Purpose: |
prototype |
ground attack |
improved
ground attack |
anti-tank |
| Engine: |
640hp
Junkers Jumo 210D |
1200hp Junkers
Jumo 211A |
1300hp
Junkers Jumo 211J |
1300hp Junkers
Jumo 211J |
| Wing
Span: |
13.0m |
13.2m |
13.8m |
13.8m |
| Length: |
10.8m |
11.0m |
11.0m |
11.0m |
| Height: |
3.90m |
3.77m |
3.77m |
3.77m |
| Wing
Area: |
30.00m? |
31.90m? |
31.90m? |
31.90m? |
| Empty
Weight: |
2273kg |
2760kg |
2810kg |
3600kg |
| Maximum
weight: |
3324kg |
4400kg |
5720kg |
5100kg |
| Maximum
Speed: |
320km/h |
350km/h |
354km/h |
344km/h |
| Dive
Speed: |
550km/h |
600km/h |
600km/h |
|
| Ceiling: |
9430m |
8100m |
9000m |
7500m |
| Climb: |
|
3000m in 8.8min |
3000m
in 14min |
3000m in 13.6min |
| Range: |
995km |
800km |
1165km |
1000km |
| Forward
Armament: |
1?7.9mm
MG17 |
2?7.9mm MG17 |
2?7.9mm
MG17 |
2?37mm BK3,7 |
| Rear
Armament: |
1?7.9mm
MG15 |
1?7.9mm MG15 |
2?7.9mm
MG81Z |
2?7.9mm MG81Z |
| Bomb
Load: |
500kg |
1000kg |
1600kg |
none |
| CIA / KGB intelligence game. Run your own operation game.
Travel around the world and set up espionage
game, trade with state secrets, weapon systems,
spy codes, WMD, hire secretaries, agents, lawyers
and soldiers, establish secret agent stations,
cells and bases and search for criminals and
politicians. Involve in agent game. Game contains
more than 40 missions including Nuclear Game,
Cold War Game, Secret Agent, CIA Games, USAF,
Prime Minister, RAF, Bin Laden, Sa |
Ju87 D Variant
Despite the Stuka's vulnerability to enemy fighters
having been exposed during the Battle of Britain, the
Luftwaffe had no choice but to continue its development
as there was no replacement aircraft in sight. The result
was the D-series. In June 1941 the RLM ordered five
prototypes, the Ju 87 V21–25. A Daimler-Benz DB 603
powerplant was to be installed in the Ju 87 D-1, but it
did not have the power of the Jumo 211 and performed
"poorly" during tests and was dropped.[56] The
Ju 87 D-series had better streamlined oil- and
water-coolers, and an aerodynamically refined cockpit
with better visibility and space.[57] In addition, armor
protection was increased and a new dual-barrel 7.92 mm
(.312 in) MG 81Z machine gun with an extremely high rate
of fire was installed in the rear defensive position. The
engine power was increased again, the Jumo 211 J-1 or
Jumo 211P now delivering 1,420 PS (1,044 kW, 1,401 hp).
The fuel capacity of the Ju 87 D was also increased to
1,370 L (360 US gal). Tests at Rechlin revealed it made
possible a flight duration of 2 hours and 15 minutes.
With an extra two 300 L (80 US gal) fuel tanks it could
reach four hours flight time.[57] Production of the D-1
variant started in 1941 with 495 orders made. These
aircraft were delivered between May 1941 and March 1942.
The RLM wanted 832 machines produced from February 1941.
The Weserflug company was tasked with their production.
From June to September 1941, 40 Ju 87 Ds were expected to
be built, increasing to 90 thereafter.[58] Various
production problems were encountered. Just one of the
planned 48 was produced in July. Of the 25 the RLM hoped
for in August 1941, none were delivered.[58] Only in
September 1941 did the first two of the planned 102 Ju
87s roll off the production lines.[59] The shortfalls
continued to the end of 1941. During this time the WFG
plant in Bremen moved production to Berlin. Over 165 Ju
87s had not been delivered and production was only 23 Ju
87 Ds per month out of the 40 expected. By the Spring of
1942 to the end of production in 1944, 3,300 Ju 87s,
mostly D-1s, D-2s and D-5s had been manufactured.[59] The
D-series saw extensive use in the Eastern Front and the
Middle East. Bomb carrying ability was massively
increased from 500 kg (1,100 lb) in the B-version to
1,800 kg (3,970 lb) in the D-version (max load for short
ranges, overload condition), a typical bomb load ranged
from 500-1,200 kg (1,100-2,650 lb).
The D-2 was a variant used as a glider tug by converting
older D-series airframes. It was intended as the tropical
version of the D-1. It was to have heavier armour to
protect the crew from ground fire. The armour reduced its
performance and caused the Oberkommando der Luftwaffe to
"place no particular value on the production of the
D-2".[57] The D-3 was an improved D-1 with more
armour for its ground-attack role. The D-3 was converted
from D-2 status and equipped with the Jumo 211 J. A
number of Ju 87 Ds were designated D-3Ns or D-3/ trops
and fitted with night and tropical equipment.[57] The D-4
designation applied to a prototype torpedo-bomber version
which could carry a 750–905 kg (1,650-2,000 lb)
aerial torpedo carried on a PVC 1006 B racks. The D-4 was
to be converted from D-3 airframes and operated from the
aircraft carrier Graf Zeppelin.[61] Other modifications
included a flame eliminator and, unlike earlier D
variants, fitted with two 20 mm MG 151/20 cannon while
the radio operator/rear gunner's ammunition supply was
increased by 1,000 to 2,000 rounds.
The Ju 87 D-5 was based on the D-3 design and was unique
in the Ju 87 series as it had wings 0.6 metres longer
than previous variants. The powerplant was upgraded to
the Jumo 211 P in-line engine with supercharger
intercoolers. In August 1943, this was replaced with the
Jumo 211 J-1. This engine increased rate of climb by 15
m/s (2,953 ft/min). With introduction of the Jumo 213 and
increased power and climb rate, the lengthened wings were
no longer needed.[60] The window in the floor of the
cockpit was reinforced and four, rather than the previous
three, aileron hinges were installed. Higher diving
speeds were obtained of 650 km/h (408 mph) up to 2,000 m
(6,400 ft). Range was recorded as 715 km (443 mi) at
ground level and 835 km (517 mi) at 5,000 m (16,400
ft).[60]
Fuel capacity was in the form of one main 480 L (127 US
gal) fuselage tank and two wing tanks of 150 L (40 US
gal) capacity. Two 300 L (80 US gal) drop tanks could
also be installed under the wings. The D-5 was also
fitted with a 20 mm MG 151/20 cannon in each wing. Both
magazines had a capacity of 180 rounds. The radio
operator/gunner operated 7.92 mm (.312 in) MG 81Z.
Ammunition loads usually ranged from 1,400 to 2,000
rounds.[60] The D-6, according to "Operating
instructions, works document 2097", was built in
limited numbers to train pilots on "rationalised
versions". However due to shortages in raw materials
it did not go into mass production.[63] The D-7 was
another ground attack aircraft based on D-1 airframes
upgraded to D-5 standard (armor, wing cannons, extended
wing panels), while the D-8 was similar to the D-7 but
based on D-3 airframes.[63] The D-7 and D-8 were both
were fitted with flame dampers, and could conduct night
operations.
The Ju 87 E and F proposals were never built, and Junkers
went straight onto the next variant. Another variant
derived from the Ju 87 D airframe was called the Ju 87 H,
and saw service as a dual-control trainer.
In January 1943 a variety of Ju 87 Ds became "test
beds" for the Ju 87 G variants. At the start of 1943
the Luftwaffe test centre at Tarnewitz tested this
combination from a static position. Oberst G. Wolfgang
Vorwald noted the experiments were not successful, and
suggested the cannon be installed on the Messerschmitt Me
410.[64] However, testing continued, and on 31 January
1943 Ju 87 D-1 W.Nr 2552 was tested by a Hauptmann
Hans-Karl Stepp near the Briansk training area. Stepp
noted the increase in drag, which reduced the aircraft's
speed to 259 km/h (162 mph). Stepp also noted that the
aircraft was also less agile than the existing D
variants. D-1 and D-3 variants operated in combat with
the 37 mm (1.46 in) BK 37 cannon in 1943.
Ju-87-D Known prototypes
* Ju 87D V 21. Registration D-INRF. W.Nr 0870536.
Airframe conversion from B-1 to D-1. First flown on 1
March 1941.
* Ju 87D V 22 Registration SF+TY. W.Nr 0870540. Also
airframe conversion from B-1 to D-1. First flown on 1
March 1941.
* Ju 87D V 23 Registration PB+UB. W.Nr 0870542. Also
airframe conversion from B-1 to D-1. First flown on 1
March 1941.
* Ju 87D V 24 Registration BK+EE. W.Nr 0870544. Also
airframe conversion from B-1 to D-1/D-4. First flown on 1
March 1941.
* Ju 87D V 25 Registration BK+EF. W.Nr 0870530. Also
airframe conversion from B-1 to D-4 trop. First flown on
1 March 1941.
* Ju 87D V 30 is the only known prototype of the Ju 87
D-5. W.Nr 2296. First flown on 20 June 1943.
* Ju 87D V 26-28, Ju 87 V 31, and V 42-47 were
experiments of unknown variants
Ju87- C
On 18 August 1937 the RLM decided to introduce the Ju
87C. The Ju 87 G was intended to be a dive and torpedo
bomber for the Kriegsmarine. The type was ordered into
prototype production and available for testing in January
1938. Testing was given just two months and was to begin
in February and end in April 1938. The prototype V10 was
to be a fixed wing test aircraft, while the following V11
would be modified with folding wings. The prototypes were
Ju 87 B-0 airframes equipped with Jumo 211 A aero
engines. Owing to delays the V10 was not completed until
March 1938. It first flew on 17 March and was designated
Ju 87 C-1. On 12 May the V11 also flew for the first
time. By 15 December 1939 915 arrested landings on dry
land had been made. It was found the arresting gear winch
was too weak and had to be replaced. Tests showed the
average braking distance was 20–35 metres. The Ju 87
V11 was designated C-0 on 8 October 1938. It was fitted
out with standard Ju 87 C-0 equipment and better
wing-folding mechanisms. The "carrier Stuka"
was to be built at the Weserflug Company's Bremen plant
between April and July 1940. Between July 1940 and August
1941 120 Ju 87 C-1s were built.
Among the "special" equipment of the Ju 87 C
was a two seat rubber dinghy with signal ammunition and
emergency ammunition. A quick fuel dump mechanism and two
inflatable 750 L (200 US gal) bags in each wing and a
further two 500 L (130 US gal) bags in the fuselage
enabled the Ju87-C to remain floating for up to three
days in calm seas.[53] On 6 October 1939, with the war
already underway, 120 of the planned Ju 87 Tr(C)s on
order at that point were cancelled. Despite the
cancellation the tests continued using catapults. The
Ju87 C had a takeoff weight of 5,300 kg (11,700 lb) and a
speed of 133 km/h (82 mph) on departure. The Ju 87 could
be launched with a SC 500 kg (1,100 lb) bomb and four SC
50 kg (110 lb) bombs under the fuselage. The C-1 was to
have two MG 17s mounted in the wing with a MG 15 operated
by the rear gunner for defensive purposes. On 18 May
1940, production of the C-1 was switched to the R-1. The
fleet of Ju 87 Cs that existed were lost throughout the
war.
|
Unlike
the British and American Air Forces, the Luftwaffe
never developed four-engine bombers in any
significant numbers, and was thus unable to
conduct an effective long-range strategic bombing
campaign against either the Russians or the
Western Allies. The Messerschmitt Bf 109 was the
most versatile and widely-produced fighter
aircraft operated by the Luftwaffe and was
designed when biplanes were still standard. Many
versions of this aircraft were made. The engine,
a liquid cooled Mercedes-Benz DB 601, initially
generated up to almost 1,000 hp (750 kW). This
power increased as direct fuel injection was
introduced to the engines. The kill ratio (almost
9:1) made this plane far superior than any of the
other German fighters during the war. In this
regard it was followed by the Focke-Wulf Fw 190
at 4:1. This plane had relatively short wings and
was powered by a radial BMW engine. The Junkers
Ju 87 Stuka was a main asset for Blitzkrieg, able
to place bombs with deadly accuracy. The leader
of the Luftwaffe was Hermann G?ring, a World War
I fighter ace and former commander of Manfred von
Richthofen's famous JG 1 (aka "The Flying
Circus") who had joined the Nazi party in
its early stages.
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
|
| |
 |
|
| |
Turn-based WW2
naval game, extension to the classic
Submarine game (Battleship game) where
ships/planes/subs can move. Contains plenty of
game missions, game campaigns and 40 ship,
submarine, airplane ana port artillery types,
with combat maps up to 96X96 large. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Fashion Tycoon is
a business fashion management game.
You'll build your multinational fashion company,
destroy competition, hire employees, fashion
models and businessman, establish company
objects, run fashion shows and brand campaigns.
There is a more than 30 missions with different
game objectives. You can hire more than 100
fashion models, directors, brand experts,
celebrities. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Turn-based space
strategy game represents World War 4
conflict on tactical level.
The user-friendly game engine allows more than 60
unit types, including planet battleships, galaxy
cruisers, death-stars, stealth units, star
destroyers, air-space interceptors, explorers,
planet artillery and radars. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Tycoon Strategy
Game - build your own world business empire as an
arms dealer tycoon. Travel around the world,
trade with more than 400 weapon systems, hire
secretaries, bodyguards, lawyers, fighters and
tanks, establish companies and search for
criminals and hostages. |
|
| |
|
|
| In
the summer and autumn of 1940, the Luftwaffe lost
the Battle of Britain over the skies of England,
the first all-air battle. Following the military
failures on the Eastern Front, from 1942 onwards,
the Luftwaffe went into a steady, gradual decline
that saw it outnumbered and overwhelmed by the
sheer number of Allied aircraft being deployed
against it. Towards the end of the war, the
Luftwaffe was no longer a major factor, and
despite fielding advanced aircraft like the
Messerschmitt Me 262, Heinkel He 162, Arado Ar
234, and Me 163 was crippled by fuel shortages
and a lack of trained pilots. There was also very
little time to develop these aircraft, and could
not be produced fast enough by the Germans, so
the jets and rockets proved to be "too
little too late." |
|
|