USAF Plane
List
USN
FIGHTERS
A-10
Thunderbolt II
F-5 Freedom
Fighter
F-20
Tigershark
F-4 Phantom
II
F-86 Sabre,
A-4 Skyhawk,
A-6 Grumann
Intruder
F-15 Eagle
F15,
F-16
Fighting Falcon
F-18 Hornet
F-22 Raptor
F-35 Joint
Strike Fighter
U-2 Dragon
Lady
SR-71
Blackbird
F-117
Nighthawk F117
F-22 Raptor,
F-35 Joint
Strike Fighter JSF
B-52
Stratofortress B52
F-111
B-1
Lancer
B-2
Spirit
P-3C
Orion
S-3B
Viking
CH-46
Sea Knight,
CH-53
Sea Stallion
H-3
Sea King
MH-53
Sea Dragon
SH-60
Seahawk
HH/UH-1N
Iroquois
AH-1
Cobra
UH-60
Black Hawk,
HH-60
Pave Hawk Helicopter
AH-64
Apache AH64
RQ-1
Predator
List of Aircraft
Weapons
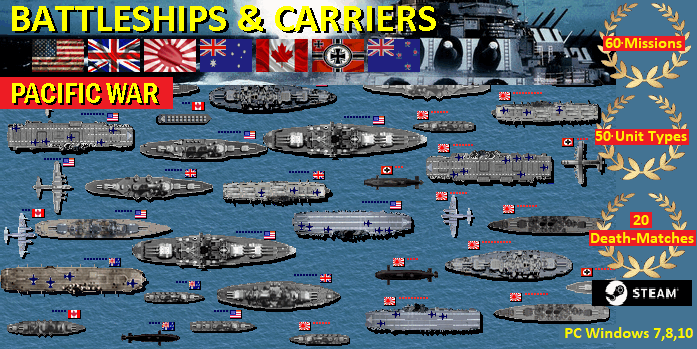
www.battle-fleet.com
Battleship Game - WW2 Naval Strategy: the best
choice among aircraft carrier games
and submarine and battleship games.
Missions and Scenarios:
Pearl Harbor Game
Atlantic Game 1943
Sink Cruisers Game
Midway Game
Iwo Jima Game
US Marines Game
Luftwaffe Game Pacific
Torpedo Game Boats
Bismarck Game Pacific
Destroy RAF Game
Okinawa
Us Navy Submarine Game
Fleet Submarines Game
Kamikaze Game
U Boat Game
Singapore Game
Swordfish Hunt
Patrol Boats
Air Supremacy
Alert
Battleships Game
Java
Defense
Fleet Cruisers Game
Atlantic Island
Coral Sea Game
Iron Sea
Mykonos
Imperial Ocean
Long Convoy
Skagerrak
Target Los Angeles
West Pacific Game
Pacific War Game
Leyte Transport
Emperor Hirohito
Normandy Game
South Pacific Game
Destroy USAF Game
Submarine Games
US Navy Game
Free Hunt Doenitz Game
Free Hunt Spruance Game
Free Hunt Halsey Game
Imperial Navy I
Royal Navy Game
Free Hunt Pearl Harbor Games
Midway II
Kriegsmarine I
Brisbane Convoy
Clear West Coast
Fall Of Australia
Battle For Leyte
Conquer Of Japan
HMAS Perth
Road To Okinawa
Orange Ports
Emperor Defense
Prince Of Wales
San Bernardino
Pacific Race
Heavy Duty
Tokio Express
Operation Sidney
Bomber Operation
Conquer Of Italy
Heavy Cruiser Game
Frigate Hunt
Santa Cruz
Lamansh Game
Azores Transport
Norway Convoy
Invasion
Grossadmiral
Norway Ports
Drang Nach Ost
Convoy Pk30
Ciano Defense
Sir John Tovey
Free Hunt Andrews
Germans On Pacific
Silent Hunt
Antigua
Return To Midway
Kriegsmarine Game II
Royal Air Force Game
F. Hunt Lancaster
Jamamoto Game
Free Hunt USN
Free Hunt Japan
Free Hunt RAAF
Free Hunt U Boat Game
Free Hunt Aircraft Carriers Game
Free Hunt Hawaii
Free Hunt Yamato Game
Free Hunt Iwo Jima Game
Free Hunt Pacific Game
Free Hunt Torpedos
Free Hunt Convoy
Free Hunt Germany
Free Hunt Germany II
Free Hunt Italy
Free Hunt Malaya
Free Hunt Subs Game
Free Hunt B-29 Game
Free Hunt USN 1944
Devil Island
Dragoon Carriers Game
|
|
F-14 Tomcat
 |
 |
 |
 |
| F14
Tomcat F-14 |
F14-A
Tomcat |
F14
Wing |
F-14
landing |
The F-14 Tomcat is a
supersonic, twin-engine, variable sweep wing, two-place
strike fighter manufactured by Grumman Aircraft
Corporation. The multiple tasks of navigation, target
acquisition, electronic counter measures (ECM), and
weapons employment are divided between the pilot and the
radar intercept officer (RIO). Primary missions include
precision strike against ground targets, air superiority,
and fleet air defense.
Features: As a Strike Fighter, the Tomcat
is capable of deploying an assortment of air-to-ground
ordnance (MK-80 series GP bombs, LGBs and JDAM) in
various configurations, while simultaneously carrying the
AIM-7, AIM-9 and AIM-54 air-to-air missiles. The F14 also
has the LANTIRN targeting system that allows delivery of
various laser-guided bombs for precision strikes in
air-to-ground combat missions and for battle damage
assessment. With its Fast Tactical Imagery (FTI) system
the F-14 can transmit and receive
targeting/reconnaissance imagery in-flight to provide
time sensitive strike capability. A number of F-14s also
carry the Tactical Air Reconnaissance Pod System (TARPS)
providing in-theater tactical reconnaissance.
Background: Current plan
is to have F14 Tomcats in service until
mid-FY07. Tomcat squadrons have already started
to transition to the F/A-18 E/F Super Hornet
aircraft, and will continue to transition in a phased
approach
| CIA / KGB intelligence game. Run your own operation game.
Travel around the world and set up espionage
game, trade with state secrets, weapon systems,
spy codes, WMD, hire secretaries, agents, lawyers
and soldiers, establish secret agent stations,
cells and bases and search for criminals and
politicians. Involve in agent game. Game contains
more than 40 missions including Nuclear Game,
Cold War Game, Secret Agent, CIA Games, USAF,
Prime Minister, RAF, Bin Laden, Sadam, KGB,
Operations Iran… |
|
F14 General Characteristics
Overall Length: 62 feet 9 inches (18.9 meters)
Wingspan: 64 feet (19 meters) unswept; 38 feet (11.4
meters) swept
Height: 16 feet (4.8 meters)
Weight: 43,600 lb (19,777 kg) (F14B)
Speed: Mach 2+
Ceiling: 50,000+ feet
Range: 1600 nm
Power Plants:
F14 A: (2) TF30-414A Afterburning Turbofans with over
40,000 lb Total Thrust
F14 B/D: (2) F110-GE400 Afterburning Turbofans with over
54,000 lb Total Thrust
Sensors: Tactical Air Reconnaissance Pod System (TARPS)
LANTIRN Targeting System
Armament: Up to 13,000 pounds to include fourJoint Direct
Attack Munitions (JDAM) [F-14D], AIM-54 Phoenix missile,
AIM 7 Sparrow missile, AIM 9 Sidewinder missile ,
air-to-ground precision strike ordnance, and one M61A1/A2
Vulcan 20mm cannon.
Crew: Two (pilot and radar intercept officer)
Contractor: Northrop Grumman
F14 Date Deployed: First flight: December 1970
F14
Operational history
The F-14 Tomcat was the Navy's primary air superiority
fighter and tactical reconnaissance platform from 1972 to
2006. The F-14 has served in Iran's Air Force from 1978
to the present day.
United States Navy
The F-14 began replacing the F-4 Phantom II in USN
service starting in September 1974 with squadrons VF-1
Wolfpack and VF-2 Bounty Hunters aboard USS Enterprise
and participated in the American withdrawal from Saigon.
The F-14 had its first kills on 19 August 1981 over the
Gulf of Sidra in what is known as the Gulf of Sidra
incident after two F-14s from VF-41 Black Aces were
engaged by two Libyan Su-22 "Fitters". The
F-14s evaded the short range heat seeking AA-2
"Atoll" missile and returned fire, downing both
Libyan aircraft. U.S. Navy F-14s once again were pitted
against Libyan aircraft on 4 January 1989, when two F-14s
from VF-32 shot down two Libyan MiG-23
"Floggers" over the Gulf of Sidra in a second
Gulf of Sidra incident.
Despite the attention given to the Tomcat over aerial
encounters in the Gulf of Sidra, its first sustained
combat baptism of fire was as a photo reconnaissance
platform. The Tomcat was selected to inherit the
Reconnaissance mission upon departure of the dedicated
RA-5C Vigilante and RF-8G Crusaders from the fleet. A
large pod called the Tactical Airborne Reconnaissance Pod
System (TARPS) was developed and fielded on the Tomcat in
1981. With the retirement of the last RF-8G Crusaders in
1982, TARPS F-14s became the U.S. Navy's primary tactical
reconnaissance system. One of two Tomcat squadrons per
airwing was designated as a TARPS unit and received 3
TARPS capable aircraft and training for 4 TARPS aircrews.
An F-14A Tomcat from VF-114 intercepting a Soviet Tu-95RT
"Bear-D" maritime patrol aircraft.
While the Tomcat was being used by Iran in combat against
Iraq in its intended air superiority mission over the
skies of Iran in the early 1980s, the US Navy found
itself flying regular daily combat missions over Lebanon
to photograph activity in the Bekaa Valley. At the time,
the Tomcat had been thought too large and vulnerable to
be used overland, but the need for imagery was so great
that Tomcat aircrews developed high speed medium altitude
tactics to deal with considerable AAA and SA-7 SAM threat
in the Bekaa area. An urgent combat need was stated to
address the Tomcat vulnerability in this type of mission.
The first exposure of a Tomcat to a SA-2 was over Somalia
in April 1983 when a local battery was unaware of two
Tomcats scheduled for a TARPS missions in prelude to an
upcoming international exercise in vicinity of Berbera.
An SA-2 was fired at the second Tomcat while conducting
10 thousand foot mapping profile at max conserve setting.
The Tomcat aircrews spotted the missile launch and dove
for the deck thereby evading it without damage. The
unexpected demand for combat TARPS laid the way for high
altitude sensors such as the KA-93 36 in (91 cm) Long
Range Optics (LOROP) to be rapidly procured for the
Tomcat as well as an Expanded Chaff Adapter (ECA) to be
incorporated in a AIM-54 Phoenix Rail. Commercial
"Fuzz buster" type radar detectors were also
procured and mounted in pairs in the forward cockpit as a
stop gap solution to detect SAM radars such as the SA-6.
The ultimate solution was an upgrade to the ALR-67 then
being developed, but it would not be ready until the
advent of the F14 A+ in the latter 1980s. During the Gulf
of Sidra operations in 1986, the Tomcats were used in
over-water missions only due to their vulnerability
overland. It was not until Desert Shield that US Navy
Tomcats were introduced to overland combat operations on
a regular basis.
The participation of the F14 Tomcat in the 1991 Operation
Desert Storm consisted of Combat Air Patrol (CAP) over
the Red Sea and Persian Gulf and overland missions
consisting of strike escort and reconnaissance. Until the
waning days of Desert Storm, in-country air superiority
was tasked to USAF F-15 Eagles due to the way the Air
Tasking Orders (ATO) delegated primary overland CAP
stations to the F-15 Eagle. The governing Rules of
Engagement (ROE) also dictated a strict Identification
Friend or Foe (IFF) requirement when employing Beyond
Visual Range weapons such as the AIM-7 Sparrow and
particularly the AIM-54 Phoenix. This hampered the Tomcat
from using its most powerful weapon. Furthermore, the
powerful emissions from the AWG-9 radar are detectable at
great range with a radar warning receiver. Iraqi fighters
routinely displayed countertactics as soon as the Tomcats
"lit them up" with the AWG-9. The US Navy
suffered its only F14 loss from enemy action on 21
January 1991 when b/n 161430, an F-14 A upgraded to an
F-14A+, from VF-103 was shot down by an SA-2
surface-to-air missile while on an escort mission near Al
Asad airbase in Iraq. Both crew survived ejection with
the pilot being rescued by USAF Special Operations Forces
and the RIO being captured and held by Iraqi troops as a
POW until the end of the war. The F-14 also achieved its
final kill, an Mi-8 "Hip" helicopter, with an
AIM-9 Sidewinder.
In 1995, F-14s from V-F14 and VF-41 participated in
Operation Deliberate Force as well as Operation Allied
Force in 1999, and in 1998, VF-32 and VF-213 participated
in Operation Desert Fox. On 15 February 2001 the Joint
Direct Attack Munition or JDAM was added to the Tomcat's
arsenal. On 7 October 2001 F-14s would lead some of the
first strikes into Afghanistan marking the start of
Operation Enduring Freedom and the first F14 drop of a
JDAM occurred on 11 March 2002. F-14s from VF-2, VF-31,
VF-32, VF-154, and VF-213 would also participate in
Operation Iraqi Freedom. The F-14Ds of VF-2, VF-31, and
VF-213 obtained JDAM capability in March 2003.[15] On 10
December 2005, the F14-Ds of VF-31 and VF-213 were
upgraded with a ROVER III downlink for transmitting
images to a ground Forward Air Controller (FAC). The
F-14s of VF-31 and VF-213 deployed on their last combat
cruise on USS Theodore Roosevelt in 2005.
F14 Variants
A total of 712 F-14s were built at Grumman's factory in
Calverton on Long Island from 1969 to 1991. While the
F-14 is listed as being produced in Bethpage, NY all
construction and test flights were performed out of
Grumman's Calverton facility. The Bethpage facility was
home to the engineers who designed the F-14 and it
produced WW2 aircraft. But Bethpage no longer had the
facilities or airport required to produce such a large
airplane.
* YF-14A: Prototypes and pre-production aircraft, 12
built.
* F-14A : The original production two-seat all-weather
interceptor fighter version for the US Navy.
Modifications late in its service life added precision
strike munitions to its armament. 545 F-14A aircraft were
delivered to the US Navy and 79 to Iran. The final 102
F14 As were delivered with improved TF30-P-414A engines.
Additionally, an 80th F14 A was manufactured for Iran,
but was delivered to the US Navy.
* F-14A Plus or F14 B: Upgraded version of the F-14A with
GE F110-400 engines. Much of the avionics as well as the
AWG-9 radar were retained. Later re-designated F14 B.
Thirty eight new aircraft were manufactured and 48 F-14A
were upgraded to B variants.[28] In the late 1990s, 67
F14 Bs were upgraded to extend airframe life and improve
offensive and defensive avionics systems. The modified
aircraft became known as F-14B Upgrade aircraft.
* F-14D Super Tomcat: The final incarnation of the F-14.
The original TF-30 engines were replaced with GE F110-400
engines, similar to the F-14B. The F-14D also included
newer digital avionics systems including a Glass cockpit
and replaced the AWG-9 with the newer APG-71 radar. A
total of 37 new aircraft were constructed and 18 F14 A
were upgraded to D variants.
F14 Operators
* Pacific Fleet
o F-14 VF-1 Wolfpack (Disestablished 30 September 1993)
o F-14 VF-2 Bounty Hunters (Redesignated VFA-2 with
F/A-18F 1 July 2003)
o F-14 VF-21 Freelancers (Disestablished 31 January 1996)
o F-14 VF-24 Fighting Renegades (Disestablished 20 August
1996)
o F-14 VF-51 Screaming Eagles (Disestablished 31 March
1995)
o F-14 VF-111 Sundowners (Disestablished 31 March 1995)
o F-14 VF-114 Aardvarks (Disestablished 30 April 1993)
o F-14 VF-124 Gunfighters (Disestablished 30 September
1994)
o F-14 VF-154 Black Knights (Redesignated VFA-154 with
F/A-18F 1 October 2003)
o F-14 VF-191 Satan's Kittens (Disestablished 30 April
1988)
o F-14 VF-194 Red Lightnings (Disestablished 30 April
1988)
o F-14 VF-201 Hunters (Redesignated VFA-201 with F/A-18A
1 January 1999)
o F-14 VF-202 Superheats (Disestablished 31 December
1999)
o F-14 VF-301 Devil's Disciples (Disestablished 11
September 1994)
o F-14 VF-302 Stallions (Disestablished 11 September
1994)
* Atlantic Fleet
o F-14 VF-11 Red Rippers (Redesignated to VFA-11 with
F/A-18F in May, 2005)
o F-14 V F14 Tophatters (Redesignated VFA-14 with F/A-18E
1 December 2001)
o F-14 VF-31 Tomcatters (Redesignated VFA-31 with F/A-18E
October, 2006)
o F-14 VF-32 Swordsmen (Redesignated VFA-32 with F/A-18F
on 1 October 2005)
o F-14 VF-33 Starfighters (Disestablished 1 October 1993)
o F-14 VF-41 Black Aces (Redesignated VFA-41 with
F/A-18F, 1 December 2001)
o F-14 VF-74 Bedevilers (Disestablished 30 April 1994)
o F-14 VF-84 Jolly Rogers (Disestablished 1 October 1995)
o F-14 VF-101 Grim Reapers (Disestablished 15 September
2005)
o F-14 VF-102 Diamondbacks (Redesignated VFA-102 with
F/A-18F in 1 May 2002)
o F-14 VF-103 Sluggers/Jolly Rogers (Redesignated VFA-103
with F/A-18F 1 May 2005)
o F-14 VF-142 Ghostriders (Disestablished 30 April 1995)
o F-14 VF-143 Pukin' Dogs (Redesignated V F14 with
F/A-18E in early 2005)
o F-14 VF-211 Fighting Checkmates (Redesignated VFA-211
with F/A-18F 1 October 2004)
o F-14 VF-213 Black Lions (Redesignated VFA-213 with
F/A-18F in May 2006)
* Test and Evaluation Squadrons
o F-14 VX-4 Evaluators (Disestablished 30 September 1994)
o F-14VX-9 Vampires (Currently operates F/A-18C/D/E/F,
EA-6B, AV-8B, & AH-1)
o F-14 VX-23 Salty Dogs (Currently operates
F/A-18C/D/E/F, EA-6B, EA-18G & T-45)
Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force (IRIAF) squadrons
* 72nd TFS: F14 A, 1976 - 1980
* 73rd TFS: F14 A, 1977 - until mid-1990s
* 81st TFS: F14 A, 1977 - until today
* 82nd TFS: F14 A, 1978 - until today
* 83rd TFS: F14 A, re-named former 73rd TFS[29]
F-14s preserved at museums include:
* Number Model - Location. Significance
* (R): Signifies an F-14 B or D manufactured from an F14
A.
* 157982 Y F14 A - Cradle of Aviation Museum, Garden
City, NY. Prototype #3 Nonstructural Demonstration
Testbed
* 157984 Y F14 A - National Museum of Naval Aviation,
Pensacola, FL. Prototype #5 Systems Compatibility
Demonstrator/Testbed
* 157986 Y F-14 A/B - Intrepid Sea-Air-Space Museum, New
York City, NY. Prototype #7 Engine/F-14B Testbed
* 157990 Y F-14 A - The March Field Air Museum,
Riverside, CA. Prototype #11 Avionics Testbed
* 158978 F14 A - San Diego Aircraft Carrier Museum on
board the USS Midway, San Diego, CA
* 159432 F-14 A - Cradle of Aviation Museum, Garden City,
NY. Forward Fuselage preserved
* 159610 F14 D(R) - National Air & Space Museum,
Washington DC. One of the F-14s involved in the second
Gulf of Sidra incident.
* 159624 F14 A - Wings Over the Rockies Air Museum,
Denver, Colorado
* 160382 F14 A - Museum of Flight, Seattle, WA
* 160395 F-14 A - Kalamazoo Aviation History Museum,
Kalamazoo, MI
* 160666 F-14 A - Western Aerospace Museum, Oakland, CA
* 160684 F14 A - Pima Air & Space Museum, Tucson, AZ
* 160889 F14 A - Pacific Coast Air Museum, Santa Rosa, CA
* 160899 F14 A - Cradle of Aviation Museum, Garden City,
NY
* 160902 F-14 A - Grumman Memorial Park, Calverton, NY
* 161163 F14 D(R) - Prairie Aviation Museum, Bloomington,
IL
* 161166 F14 D(R) - Carolinas Aviation Museum, Charlotte,
NC. VF-213, Last F-14 to launch on a combat mission (Iraq
February 2006)
* 161422 F-14 B(R) - Naval Air Station Wildwood Aviation
Museum, Cape May, NJ
* 161426 F-14 D(R) - DeLand Naval Air Station Museum,
DeLand, FL
* 161598 F-14 A - Tulsa Air and Space Museum, Tulsa, OK.
Has squadron VF-41, "Black Aces" markings
* 161605 F14 A - Wings Of Eagles Discovery
Center/National Warplane Museum, Horseheads, NY
* 162689 F-14A - USS Hornet Museum, Alameda, CA, VF-101
"Grim Reapers", retired August 31, 2000
* 162912 F14 B - Grissom Air Museum, Peru IN. First
aircraft retired from VF-11 Red Rippers
* 163904 F14 D - Hickory Regional Airport, Hickory, NC.
VF-31 Modex 107, Tomcat flown at Sunset Ceremony at NAS
Oceana
* 164601 F14 D - Castle Air Museum, Atwater, CA
* 164603 F14 D - American Air Power Museum, Farmingdale,
NY. VF-31 Modex 101 Last (American) Tomcat to take flight
* 164604 F14 D - NAS Oceana, Virginia Beach, VA. Last
F-14 built by Grumman.
* (unknown) F-14 - Palm Springs Air Museum, Palm Springs,
CA.
* (unknown) F14 A - Aviation Challenge Camp, Huntsville,
AL. Has the "Jolly Rogers" Insignia on left
tail - Once on 3-day stand-by
F14 Retirement
The F-14 has been completely
retired from US Naval service. At one point, it was
slated to remain in service through at least 2008, but
all F-14A and F-14B airframes had already been retired,
and the last two squadrons, the VF-31 Tomcatters and the
VF-213 Black Lions, both flying the D models, arrived for
their last fly-in at Naval Air Station Oceana on 10 March
2006.
The last American F-14 to takeoff from a US Navy carrier,
USS Theodore Roosevelt on 28 July 2006
The last American F-14 combat mission was completed on 8
February 2006, when a pair of Tomcats landed aboard the
USS Theodore Roosevelt (CVN-71) after one dropped a bomb
in Iraq. That aircraft was assigned to VF-31 and the
aircrew credited with the last bomb dropped in combat by
a Navy Tomcat was pilot LT Justin Halligan and RIO LT
Bill Frank. The other Tomcat on that mission was an F-14D
from VF-213 piloted by Commander, Carrier Air Wing Eight,
Capt. William G. Sizemore, and became the last F-14 to
land on an aircraft carrier after a combat mission.
During their final deployment with the USS Theodore
Roosevelt (CVN-71), VF-31 and VF-213 collectively
completed 1,163 combat sorties totaling 6,876 flight
hours, and dropped 9,500 lb (4,300 kg) of ordnance during
reconnaissance, surveillance, and close air support
missions in support of Operation Iraqi Freedom.[46]
The last American F-14 to fly a combat mission, an F14
D(R) from VF-213, lands at Sherman Field at Naval Air
Station Pensacola, Florida.
On 10 March 2006, the 22 planes from these squadrons flew
in formation into Naval Air Station Oceana after the last
deployment of the F-14. VF-31 remained operational in the
F-14 Tomcat under the Fleet Response Plan (FRP) through
September and conducted the last carrier qualifications
in late July maintaining their ability to deploy right up
until the end. VF-213 and VF-31 would transition to the
Super Hornet training.
The USS Theodore Roosevelt (CVN-71) shot from its
catapult an F14 D, assigned to VF-31, for the last time
on 28 July 2006. It was piloted by Lt. Blake Coleman and
Lt. Cmdr Dave Lauderbaugh as RIO.[47] The last trap
recovery was made a while before by Lt. Chris Rattigan
and Lt. Paul Dort, on aircraft no. 110. The
"official" final flight retirement ceremony was
on 22 September 2006 at Naval Air Station Oceana. The
ceremonial last flight was flown by Lt. Cmdr. Chris
Richard and Lt. Mike Petronis as RIO in a backup F-14
(Felix 107),[48] after the primary aircraft experienced a
mechanical problem.[49] The actual last flight of the
F-14 Tomcat in U.S. service took place 4 October 2006,
when an F-14D of VF-31 was ferried from Oceana to
Republic Airport on Long Island, NY.
The remaining intact US Navy F-14 aircraft have been
stored at the 309th Aerospace Maintenance and
Regeneration Group "Boneyard", at Davis-Monthan
Air Force Base, Arizona. By July 2007, many of the
remaining 165 aircraft were being shredded to prevent
parts from being acquired by Iran, the only other nation
to buy the F-14. By July 2007, 23 F-14s had been shredded
at a cost of US$900,000. Due to the strength of the
landing gear, it was removed before shredding and cut up
with a torch. The last remaining F-14 after demolition
will be located at Naval Air Station Pensacola, Florida.
Text is available under the terms of the GNU Free
Documentation License
|
F-14
The F-14 has been completely retired from US Naval
service. At one point, it was slated to remain in service
through at least 2008, but all F-14A and F-14B airframes
had already been retired, and the last two squadrons, the
VF-31 Tomcatters and the VF-213 Black Lions, both flying
the D-models, arrived for their last fly-in at Naval Air
Station Oceana on 10 March 2006.[32]
The last American F-14 to fly a combat mission, an F-14 D
(R) from VF-213, lands at Sherman Field at Naval Air
Station Pensacola, Florida.
The last American F14
combat mission was completed on 8 February 2006, when a
pair of Tomcats landed aboard the USS Theodore Roosevelt
after one dropped a bomb in Iraq. That aircraft was
assigned to VF-31 and the aircrew credited with the last
bomb dropped in combat by a Navy Tomcat was pilot Lt.
Justin Halligan and RIO Lt. Bill Frank. The other Tomcat
on that mission was an F-14D from VF-213 piloted by
Commander, Carrier Air Wing Eight, Capt. William G.
Sizemore, and became the last F-14 to land on an aircraft
carrier after a combat mission. During their final
deployment with the USS Theodore Roosevelt, VF-31 and
VF-213 collectively completed 1,163 combat sorties
totaling 6,876 flight hours, and dropped 9,500 pounds
(4,300 kg) of ordnance during reconnaissance,
surveillance, and close air support missions in support
of Operation Iraqi Freedom.
| |
 |
 |
| Turn-based WW2
naval game, extension to the classic
Submarine game (Battleship game) where
ships/planes/subs can move. Contains plenty of
game missions, game campaigns and 40 ship,
submarine, airplane ana port artillery types,
with combat maps up to 96X96 large. |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
 |
Turn-based space
strategy game represents World War 4
conflict on tactical level.
The user-friendly game engine allows more than 60
unit types, including planet battleships, galaxy
cruisers, death-stars, stealth units, star
destroyers, air-space interceptors, explorers,
planet artillery and radars. |
| |
| |
 |
| Tycoon Strategy
Game - build your own world business empire as an
arms dealer tycoon. Travel around the world,
trade with more than 400 weapon systems, hire
secretaries, bodyguards, lawyers, fighters and
tanks, establish companies and search for
criminals and hostages. |
| |
On 10 March 2006, the 22 planes from these squadrons flew
in formation into Naval Air Station Oceana after the last
deployment of the F-14. VF-31 remained operational in the
F-14 Tomcat under the Fleet Response Plan (FRP) through
September and conducted the last carrier qualifications
in late July maintaining their ability to deploy right up
until the end. VF-213 and VF-31 would transition to the
Super Hornet training.
The USS Theodore Roosevelt (CVN-71) shot from its
catapult an F-14D, assigned to VF-31, for the last time
on 28 July 2006. It was piloted by Lt. Blake Coleman and
Lt. Cmdr Dave Lauderbaugh as RIO. The last trap recovery
was made a while before by Lt. Chris Rattigan and Lt.
Paul Dort, on aircraft no. 110. The "official"
final flight retirement ceremony was on 22 September 2006
at Naval Air Station Oceana. The ceremonial last flight
was flown by Lt. Cmdr. Chris Richard and Lt. Mike
Petronis as RIO in a backup F-14 (Felix 107),[35] after
the primary aircraft experienced a mechanical
problem.[36] The actual last flight of the F-14 Tomcat in
U.S. service took place 4 October 2006, when an F-14D of
VF-31 was ferried from Oceana to Republic Airport on Long
Island, NY.
The remaining intact US Navy F-14 aircraft have been
stored at the 309th Aerospace Maintenance and
Regeneration Group "Boneyard", at Davis-Monthan
Air Force Base, Arizona. By July 2007, many of the
remaining 165 aircraft were being shredded to prevent
parts from being acquired by Iran, the only other nation
to buy the F-14. By July 2007, 23 F-14s had been shredded
at a cost of $900,000. Due to the strength of the landing
gear, it was removed before shredding and cut up with a
torch. The last remaining F-14 after demolition will be
located at Naval Air Station Pensacola, Florida.
|