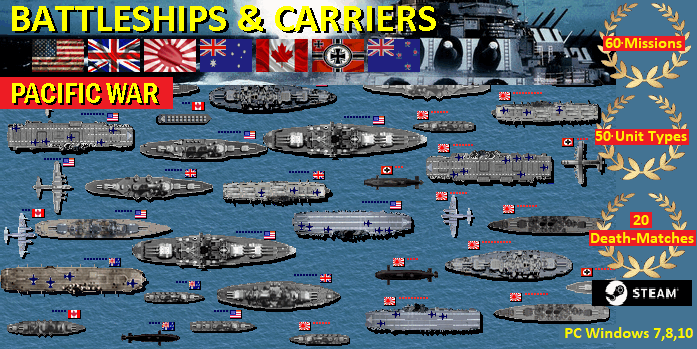
List of
German Navy Ships WW2
Battleship Bismarck,
Graf
Zeppelin
Battleships Tirpitz,
Scharnhorst Admiral
Graf Spee U-Boats
Types 1, 2A, 2B, 2C, 2D
Kriegsmarine
Submarines Types U-Flak, 7A, 7B, 7C,
7C/41, 7C/42, 7D, 7F Kriegsmarine
Submarines: U-Boats Type 9A,
9B, 9C, 9C/40, 9D, 14
Submarines: Type
XXI , Type XXIII
Grand Admiral Karl
Donitz, Erich RaederHMS Prince
of Wales Battleship, HMS Repulse HMS Ark
Royal, HMS Hood
Battlecruisers Battle of
Crete - Operation Mercury
WW2 Battle
of Taranto
Battle of
Cape Matapan Battle of
Narvik Battle of the River
Plate,
Battle of Dunkirk,
Battle of the Atlantic
www.battle-fleet.com
Battleship
Game - WW2 PC Naval Strategy
Soon: also for Android, iPad, iPhone
strategy battleship games |
Battleship Game - WW2 Naval
Strategy: No1 Battleship Game for PC and No3 Aircraft Carrier Game on World Net
Missions and Scenarios:
Pearl Harbor Game
Atlantic Game 1943
Sink Cruisers Game
Midway Game
Iwo Jima Game
US Marines Game
Luftwaffe Game Pacific
Torpedo Game Boats
Bismarck Game Pacific
Destroy RAF Game
Okinawa
Us Navy Submarine Game
Fleet Submarines Game
Kamikaze Game
U Boat Game
Singapore Game
Swordfish Hunt
Patrol Boats
Air Supremacy
Alert
Battleships Game
Java
Defense
Fleet Cruisers Game
Atlantic Island
Coral Sea Game
Iron Sea
Mykonos
Imperial Ocean
Long Convoy
Skagerrak
Target Los Angeles
West Pacific Game
Pacific War Game
Leyte Transport
Emperor Hirohito
Normandy Game
South Pacific Game
Destroy USAF Game
Submarine Games
US Navy Game
Free Hunt Doenitz Game
Free Hunt Spruance Game
Free Hunt Halsey Game
Imperial Navy I
Royal Navy Game
Free Hunt Pearl Harbor Games
Midway II
Kriegsmarine I
Brisbane Convoy
Clear West Coast
Fall Of Australia
Battle For Leyte
Conquer Of Japan
HMAS Perth
Road To Okinawa
Orange Ports
Emperor Defense
Prince Of Wales
San Bernardino
Pacific Race
Heavy Duty
Tokio Express
Operation Sidney
Bomber Operation
Conquer Of Italy
Heavy Cruiser Game
Frigate Hunt
Santa Cruz
Lamansh Game
Azores Transport
Norway Convoy
Invasion
Grossadmiral
Norway Ports
Drang Nach Ost
Convoy Pk30
Ciano Defense
Sir John Tovey
Free Hunt Andrews
Germans On Pacific
Silent Hunt
Antigua
Return To Midway
Kriegsmarine Game II
Royal Air Force Game
F. Hunt Lancaster
Jamamoto Game
Free Hunt USN
Free Hunt Japan
Free Hunt RAAF
Free Hunt U Boat Game
Free Hunt Aircraft Carriers Game
Free Hunt Hawaii
Free Hunt Yamato Game
Free Hunt Iwo Jima Game
Free Hunt Pacific Game
Free Hunt Torpedos
Free Hunt Convoy
Free Hunt Germany
Free Hunt Germany II
Free Hunt Italy
Free Hunt Malaya
Free Hunt Subs Game
Free Hunt B-29 Game
Free Hunt USN 1944
Devil Island
Dragoon Carriers
|
Axis
Powers WW2
The Axis Powers is a term for the alliance led by Nazi
Germany and between that state, Italy, and Japan during
World War II. The three major powers referred to the axis
as the Rome-Berlin-Tokyo axis.
Major Axis Powers
Germany
Italy
Japan
Minor Axis Powers
Hungary
Romania
Slovakia
Bulgaria
Italy, facing opposition to its wars in Abyssinia
(Ethiopia) from the League of Nations, forged an alliance
with Nazi Germany, which had withdrawn from the League in
1933. The term was first used by Benito Mussolini, in
November 1936, when he spoke of a Rome-Berlin axis in
reference to the treaty of friendship signed between
Italy and Nazi Germany on October 25, 1936. Later, in May
1939, this relationship transformed into an alliance,
dubbed the "Pact of Steel".
The Axis was extended to include Japan as a result of the
Tripartite Treaty of September 27, 1940. The alliance was
subsequently joined by Hungary (November 20, 1940),
Romania (November 23, 1940), Slovakia's puppet government
(November 24, 1940) and Bulgaria (March 1, 1941).
Yugoslavia joined on March 25, 1941, but a
British-supported coup d'?tat two days later put
Yugoslavia's participation in question (although King
Peter II of Yugoslavia actually declared his adherence to
the treaty), leading to a Nazi occupation of Yugoslavia
in April.
In Allied usage, Finland was often referred to as an Axis
country, but it was never a signatory. Finland
characterized its relationship with Nazi Germany during
the Continuation War as co-belligerence.
Some Italians born in this time were named Roberto, which
briefly acquired a new meaning from
"Roma-Berlino-Tokio".
The Axis of Evil named by George W. Bush has the same
connotations behind it as the Axis Powers, although the
countries named are not allied with each other.
Axis Pact of
Steel
The Pact of Steel was an agreement between the
governments of Italy and Germany signed on May 22, 1939
by Galeazzo Ciano and Joachim von Ribbentrop
The pact was one of alliance in the event of
international threats; of immediate aid and military
support in the event of war, also neither country would
make peace without the agreement of the other; and of
collaboration in military and wartime production. The
pact was initially valid for ten years.
The pact was based on the assumption of war occurring in
about three years. When Germany began the conflict in
September 1939 Italy was not on a proper war footing and
had difficulty meeting its obligations and did not enter
the conflict until June 1940 with an abortive invasion of
southern France. Certain members of the Italian
government, including the signatory Ciano, were opposed
to the pact.
Anti-Comintern
Pact
The Anti-Comintern Pact was concluded between
Nazi-Germany and Japan on November 25th, 1936. The pact
was ostensibly directed against the Communist
International (Comintern) but was specifically directed
against the Soviet Union. In case of an unprovoked attack
by the Soviet Union against Germany or Japan, the two
nations agreed to consult on what measures to take
"to safeguard their common interests". It also
agreed that neither nation would make any political
treaties with the Soviet Union, and Germany also agreed
to recognize the Japanese puppet regime in Manchuria. In
1937 Italy joined the Pact, thereby forming the group
that would later lead be known as the Axis Powers.
Italy's joining was more or less a reaction against the
failed Stresa Front, the Franco-British initiative of
1935 designed to keep Nazi-Germany from extending beyond
her borders, primarily the Anschluss of Austria, where
the Nazis recently had assassinated the Italy-oriented
dictator Engelbert Dollfuss. However, in June 1935 an
Anglo-German Naval Agreement was signed, followed by
mistrust from the unknowing France and Italy.
Meanwhile, Italy invaded the African State of Abyssinia,
an act of unprovoked aggression. Nevertheless, Britain
and France hashed out a secret agreement with Italy to
give her two-thirds of Abyssinia. When this information
was leaked to the public in Britain and France, their
governments collapsed in scandal. Mussolini realized that
future governments of France and the United Kingdom will
be less accommodating. After Italy signed the
Anti-Comintern Pact, the Franco-British initiative
failed, and soon afterwards the Anschluss of Austria was
realized.
Adolf Hitler broke the terms of the pact when he signed
the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact in August 1939. He did this
because he was attempting to avoid a war on two-fronts.
By 1940 Hitler once again began to consider invading the
Soviet Union and the German foreign minister, Joachim von
Ribbentrop, was sent to negotiate a new treaty with
Japan. On September 25th, 1940, Ribbentrop sent a
telegram to Vyacheslav Molotov, the Soviet foreign
minister, informing him that Germany, Italy and Japan
were about to sign a military alliance. Ribbentrop
pointed out that the alliance was to be directed towards
the United States and not the Soviet Union. "Its
exclusive purpose is to bring the elements pressing for
America's entry into the war to their senses by
conclusively demonstrating to them if they enter the
present struggle they will automatically have to deal
with the three great powers as adversaries."
The Anti-Comintern Pact was revived in 1941, after
Germany's assault on the Soviet Union, (Operation
Barbarossa), and on November 25th its renewal for another
five years was celebrated. This time the parties were:
Germany, Japan, Italy, Hungary, Spain, Manchukuo,
Bulgaria, Croatia, Denmark, Finland, Romania, Slovakia,
and the Nanking regime in China.
| CIA / KGB Operation
Game. Run your own intelligence game.
Travel around the world and set up espionage
game, trade with state secrets, weapon systems,
spy codes, WMD, hire secretaries, agents, lawyers
and soldiers, establish secret agent stations,
cells and bases and search for criminals and
politicians. Involve in agent game. Game contains
more than 40 missions including Nuclear Game,
Cold War Game, Secret Agent, CIA Games, USAF,
Prime Minister, RAF, Bin Laden, Sadam, KGB,
Operations Iran… |
|
|
OTHER COUNTRIES
JOIN THE AXIS ALLIANCE
In July 1940, just weeks after the defeat of
France, Hitler decided that Nazi Germany would
attack the Soviet Union the following spring. In
order to secure raw materials, transit rights for
German troops, and troop contributions for the
invasion from sympathetic powers, Germany began
to cajole and pressure the southeast European
states to join the Axis. Nazi Germany offered
economic aid to Slovakia and military protection
and Soviet territory to Romania, while warning
Hungary that recent German support for Hungarian
annexations of Czechoslovak and Romanian
territory might change to the benefit of Slovakia
and Romania.
|
 |
 |
Turn-based WW2
naval game, extension to the classic
Submarine game (Battleship game) where
ships/planes/subs can move. Contains plenty of
game missions, game campaigns and 40 ship,
submarine, airplane ana port artillery types,
with combat maps up to 96X96 large.
Soon: also for Android, iPad, iPhone
strategy battleship games |
| |
| |
| |
| |
 |
| Tycoon Strategy
Game - build your own world business empire as an
arms dealer tycoon. Travel around the world,
trade with more than 400 weapon systems, hire
secretaries, bodyguards, lawyers, fighters and
tanks, establish companies and search for
criminals and hostages. |
| |
Italy’s failed effort to conquer Greece in the late
autumn and winter of 1940-1941 exacerbated German
concerns about securing their southeastern flank in the
Balkans. Greek entry into the war and victories in
northern Greece and Albania allowed the British to open a
Balkan front against the Axis in Greece that might
threaten Romania’s oil fields, which were vital to
Nazi Germany’s invasion plans. To subdue Greece and
move the British off the European mainland, Nazi Germany
now required troop transport through Yugoslavia and
Bulgaria.
After the Italo-Greek front opened on October 28, 1940,
German pressure on Hungary and the Balkan States
intensified. Hoping for preferential economic treatment,
mindful of recent German support for annexation of
northern Transylvania, and eager for future Axis support
for acquiring the remainder of Transylvania, Hungary
joined the Axis on November 20, 1940. Having already
requested and received a German military mission in
October 1940, the Romanians joined on November 23, 1940.
They hoped that loyal support for a German invasion of
the Soviet Union and faithful oil deliveries would
destroy the Soviet threat, return the provinces annexed
by the Soviet Union in June 1940, and win German support
for the return of northern Transylvania. Both politically
and economically dependent on Germany for its very
existence as an “independent” state, Slovakia
followed suit on November 24.
Bulgaria, whose leaders were reluctant to get involved in
a war with the Soviet Union, and Yugoslavia, which was
nominally an ally of Greece, stalled, resisting German
pressure. After the Germans offered Greek territory in
Thrace and exempted it from participation in the invasion
of the Soviet Union, Bulgaria joined the Axis on March 1,
1941. When the Germans agreed to settle for Yugoslav
neutrality in the war against Greece, without demanding
transit rights for Axis troops, Yugoslavia reluctantly
joined the Axis on March 25, 1941. Two days later,
Serbian military officers overthrew the government that
had signed the Tripartite Pact. After the subsequent
invasion and dismemberment of Yugoslavia by Germany,
Italy, Hungary, and Bulgaria in April, the newly
established and so-called Independent State of Croatia
joined the Axis on June 15, 1941.
On June 26, 1941, four days after the Axis invasion of
the Soviet Union, Finland, seeking to regain territory
lost during the 1939-1940 Winter War, entered the war
against the USSR as a “co-belligerent.” Finland
never signed the Tripartite Pact.
After Japan’s surprise attack on the United States
fleet anchored at Pearl Harbor in Hawaii on December 7,
1941, and the declaration of war on the United States by
Germany and the European Axis powers within a week, the
Atlantic and Pacific wars became a truly world war.
AXIS DEFEAT
The Allied Powers, led by Great Britain, the United
States, and the Soviet Union, defeated the Axis in World
War II. Italy was the first Axis partner to give up: it
surrendered to the Allies on September 8, 1943, six weeks
after leaders of the Italian Fascist Party deposed
Fascist leader and Italian dictator Benito Mussolini. On
August 23, 1944, following the overthrow of dictator
Marshal Ion Antonescu, Romania switched sides: Romanian
troops fought alongside Soviet troops for the remainder
of the war. After the Soviets rejected its offer of an
armistice, Bulgaria surrendered on September 8, 1944, as
the Communist-led Fatherland Front seized power from the
Axis government in a coup and then declared war on Nazi
Germany. On September 19, 1944, Finland signed an
armistice with the Soviet Union.
The German occupation of Hungary in March 1944 succeeded
in its primary purpose: to prevent the Hungarian leaders
from deserting the Axis as the Romanians would later do.
Hungary never surrendered; the war ended for Hungary only
when Soviet troops drove the last pro-Axis Hungarian
troops and police units and the members of the Arrow
Cross government across Hungary’s western border
into Austria in early April 1945. Slovakia, which German
troops occupied in the summer of 1944 to suppress the
Slovak uprising, remained in the Axis as a puppet state
until the Soviets captured the capital, Bratislava, in
early April. Fanatical remnants of the Croat Ustasa
remained in Croatia until Tito’s Partisans captured
or drove them across the border into German-occupied
Slovenia and Austria itself in the last days of April
1945.
On May 7, 1945, seven days after Hitler committed
suicide, Nazi Germany surrendered unconditionally to the
Allies. Japan fought on alone, surrendering formally on
September 2, 1945.
|